Appearance
USB to RS-485/422 Converter User Manual

1. Product Overview
USB to RS-485/422 Converter is powered directly from the USB port and is compatible with USB, RS-422, and RS-485 standards. The converter transforms single-ended USB signals into balanced differential RS-422/RS-485 signals and integrates automatic direction control for the serial data flow.
Key characteristics:
- No external power supply required (USB powered)
- Support for both RS-485 (2-wire half-duplex) and RS-422 (4-wire full-duplex)
- Automatic transmit/receive direction control (no RTS/DTR wiring)
- Suitable for point-to-point and point-to-multipoint communication
- Up to 32 RS-422/RS-485 devices per converter in multi-drop mode
- Long-distance transmission over twisted-pair cabling
2. Key Features
- USB to RS-485/RS-422 converter in a compact inline form factor
- USB V1.1 and EIA RS-485/RS-422 compliant
- Asynchronous serial communication
- 2-wire half-duplex (RS-485) and 4-wire full-duplex (RS-422)
- Automatic data flow direction control (no handshake signals)
- Data rate up to 921.6 kbps on RS-485/RS-422 side (under typical conditions)
- RS-485/RS-422 transmission distance up to 1200 m at 9600 bps
- Built-in surge and ESD protection on serial lines
- USB-A male connector (host side) and DB9 male connector (field side)
- Wide operating temperature and humidity range
- Compatible with multiple Windows versions and Linux
3. Technical Parameters
This section summarizes the main performance parameters described in the original user manual.
- Standards: conforms to USB V1.1/1.0 and EIA RS-485/RS-422, backward compatible
- USB signals: VCC, DATA+, DATA-, GND, FG
- RS-485 signals: T+, T-, GND
- RS-422 signals: T+, T-, R+, R-, GND
- Working modes: asynchronous, point-to-point or point-to-multipoint, 2-line half-duplex and 4-line full-duplex
- Direction control: automatic data stream control with automatic recognition and control of the transmission direction
- Baud rate: 300–128000 bps, with automatic detection of the serial interface signal rate
- Workload capability: supports point-to-multipoint, up to 32 RS-422 or RS-485 interface devices connected to one converter
- Transmission distance:
- RS-485/RS-422 side: up to 1200 m at 9600 bps
- USB side: up to 5 m
- Protection:
- Approx. 600 W lightning strike and surge protection per line
- Up to 5 kV electrostatic protection
- TVS devices and discharge tubes are used on RS-422/RS-485 interfaces; under normal conditions the TVS remains high impedance, while under transient high energy it clamps voltage quickly and protects downstream circuitry, with small inter-pole capacitance to maintain high-speed transmission
- Interface forms:
- USB: standard USB interface connector
- Field side: RJ-45 and DB9 male connectors are referenced for RS-422/RS-485 connections in the original manual
- Transmission media: twisted-pair cable or shielded cable
- Transmission rate vs. distance (typical guidance):
- 128000 bps: up to ~300 m
- 38400 bps: up to ~600 m
- 9600 bps: up to ~1200 m
- Dimensions (from extracted text): approx. 1500 mm cable length, body size around 36 mm × 16 mm (exact mechanical drawing not provided in text)
- Working environment: -25 °C to +70 °C, relative humidity 5%–95%
- System support: Windows 95/98/2000/XP/Vista/Win7/Win8/8.1/10 and Linux; the original text also mentions IMAG as an additional environment
The original manual also refers to this product as an industrial photoelectric isolation interface converter, indicating the presence of isolation between USB and RS-485/RS-422 sides.
4. Typical Applications
- Connecting PLCs, inverters and meters with RS-485/RS-422 ports to a PC via USB
- Providing an RS-485/RS-422 port for laptops that only support USB
- Building RS-485 multi-drop acquisition networks using a USB host
- On-site commissioning and debugging of RS-422/RS-485 field devices
- Long-distance serial communication between control room and field equipment
5. Interfaces and Pin Assignment
5.1 USB Interface (Host Side)
- Connector type: USB-A male
- Function: provides both power and data connection to the host PC
- Recommended USB cable length: up to 5 m (standard USB cable)
5.2 RS-485/RS-422 Interface (Field Side)
- Connector type: DB9 male
- Transmission media: twisted-pair cable or shielded twisted-pair cable
DB9 pin assignment (RS-485/RS-422 side):
| Pin | Signal | Description | RS-422 full-duplex wiring | RS-485 half-duplex wiring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T/R+ | Transmit/Receive A+ | RS-422 TX(A+) | RS-485 (A+) |
| 2 | T/R- | Transmit/Receive B- | RS-422 TX(😎 | RS-485 (😎 |
| 3 | RXD+ | Receive A+ | RS-422 RX(A+) | — |
| 4 | RXD- | Receive B- | RS-422 RX(😎 | — |
| 5 | GND | Signal ground | GND | GND |
| 6 | N/A | Reserved / not used | — | — |
| 7 | N/A | Reserved / not used | — | — |
| 8 | N/A | Reserved / not used | — | — |
| 9 | N/A | Reserved / not used | — | — |
6. Operating Modes
This product supports the following communication modes:
- RS-422 point-to-point, 4-wire full-duplex
- RS-422 point-to-multipoint, 4-wire full-duplex
- RS-485 point-to-point, 2-wire half-duplex
- RS-485 point-to-multipoint, 2-wire half-duplex
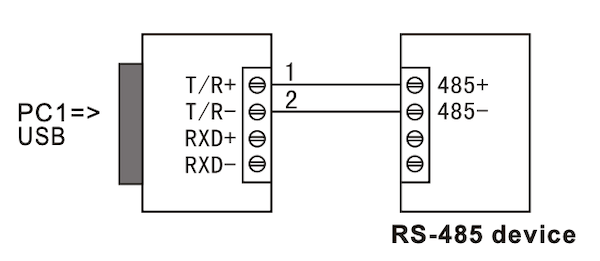
6.1 RS-485 Half-Duplex Wiring (2-Wire)
- Use T/R+ (pin 1) and T/R- (pin 2) as the A+/B- differential pair
- GND (pin 5) should be connected to the reference ground of the RS-485 network
- For point-to-multipoint buses, connect all A+ lines together and all B- lines together
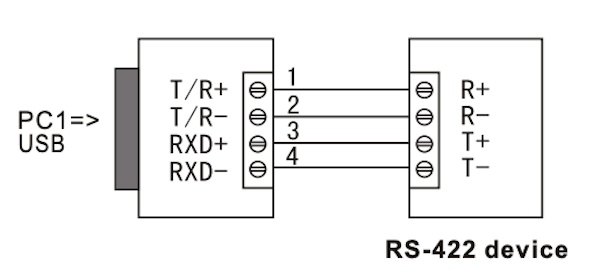
6.2 RS-422 Full-Duplex Wiring (4-Wire)
- Use T/R+ (pin 1) and T/R- (pin 2) as the transmit pair (TX+ / TX-)
- Use RXD+ (pin 3) and RXD- (pin 4) as the receive pair (RX+ / RX-)
- GND (pin 5) as common signal ground
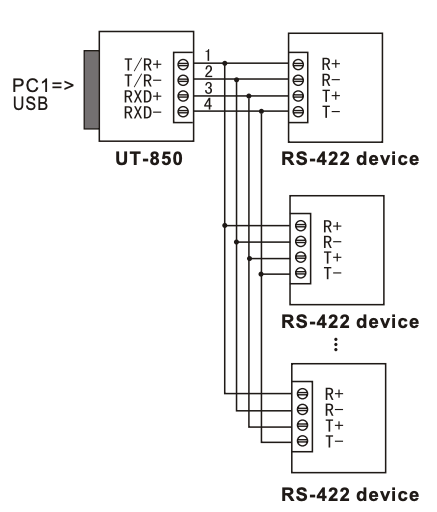
- For multi-drop RS-422, multiple receivers can be connected on the RX lines
6.3 Termination and Line Matching
To avoid signal reflection and interference in both RS-422 and RS-485 modes:
- Place a proper termination resistor (typically 120 Ω, 1/4 W) at the far end of the line
- For long buses and high noise environments, consider adding bias resistors and ensuring a proper grounding scheme
7. Hardware Installation
Preparation
- Read this manual carefully before installation.
- Check that the converter and cables are not mechanically damaged.
Connecting to the PC
- Plug the USB-A connector of the USB to RS-485/422 Converter into a USB port on the host computer.
- The converter is powered from USB and typically does not require an external power supply.
Connecting the RS-485/RS-422 Side
- Decide whether the application uses RS-485 (2-wire) or RS-422 (4-wire) mode.
- For RS-485:
- Connect T/R+ to the bus A+ line and T/R- to the bus B- line.
- Connect GND to the common ground of the RS-485 network.
- For RS-422:
- Connect T/R+ / T/R- as the transmit pair to the RS-422 device RX+ / RX-.
- Connect RXD+ / RXD- as the receive pair to the RS-422 device TX+ / TX-.
- Connect GND as the reference ground.
Multi-Drop Installations
- For RS-485:
- All nodes share a single twisted-pair bus (T/R+ and T/R-), with termination at both ends.
- Up to 32 devices can typically be connected to one USB to RS-485/422 Converter.
- For RS-422:
- TX pair is driven by the converter, RX pair aggregates multiple receivers.
- Check the loading capability of the RS-422 receivers.
- For RS-485:
Checking Indicators
- Power indicator LED should be on when the converter is powered by USB.
- Data traffic LEDs (if present) should flicker when data is sent or received.
8. Communication Settings
For proper communication, configure the serial parameters on the host and device side consistently:
- Baud rate (e.g. 9600, 19200, 38400, 115200 bps, etc.)
- Data bits (typically 8)
- Stop bits (1 or 2)
- Parity (None, Even or Odd)
Guidance from the original documents:
- Recommended distance vs. baud rate:
- 128000 bps: up to ~300 m
- 38400 bps: up to ~600 m
- 9600 bps: up to ~1200 m
9. Troubleshooting
9.1 Data Communication Failure
If communication cannot be established:
- Check that the USB cable is correctly connected and not damaged.
- Confirm that the RS-485/RS-422 interface cable is correctly wired.
- Ensure that the host PC and all field devices are powered correctly.
- Verify that wire terminal connections (A+/B-, RXD+/RXD-, GND) are correct.
- Observe the indicator LEDs to see whether they flash when receiving and sending data.
9.2 Data Loss or Incorrect Data
If data is missing or corrupted:
- Re-check the serial settings (baud rate, data bits, parity, stop bits) on both the host and device side.
- Confirm that termination resistors and grounding are properly implemented.
- Ensure that the cable length and wiring topology are appropriate for the selected baud rate.
- Check for strong electromagnetic interference sources near the cable routing.
10. Communication Connection Examples
10.1 USB to RS-422, 4-Wire Full Duplex
| Point to Point | Point to Multipoint |
|---|---|
 |  |
10.2 USB to RS-485, 2-Wire Half Duplex
| Point to Point | Point to Multipoint |
|---|---|
 | 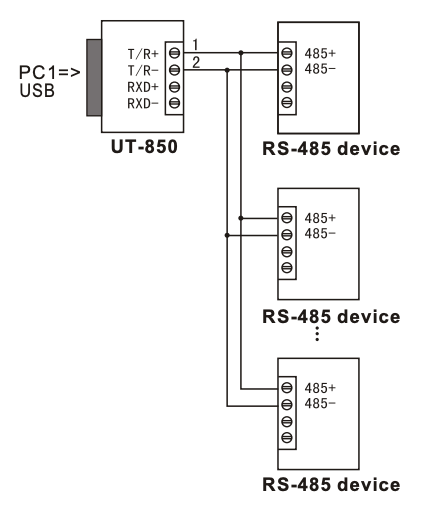 |
10.3 Connection Between Two Converters
| Full Duplex | Half Duplex |
|---|---|
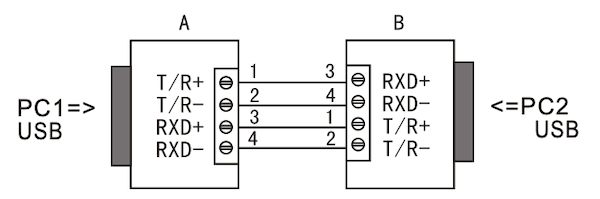 | 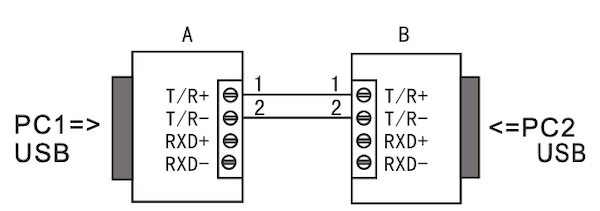 |
11. System Compatibility and Drivers
This product supports:
- Windows 95 / 98 / 2000 / XP / Vista / 7 / 8 / 8.1 / 10
- Linux distributions
The converter typically uses a Prolific PL2303TA (or similar) USB-to-serial bridge. Driver support may vary by OS version; always refer to the latest manufacturer driver package when deploying in a new environment.