Appearance
Mini LoRa DTU (Y210)
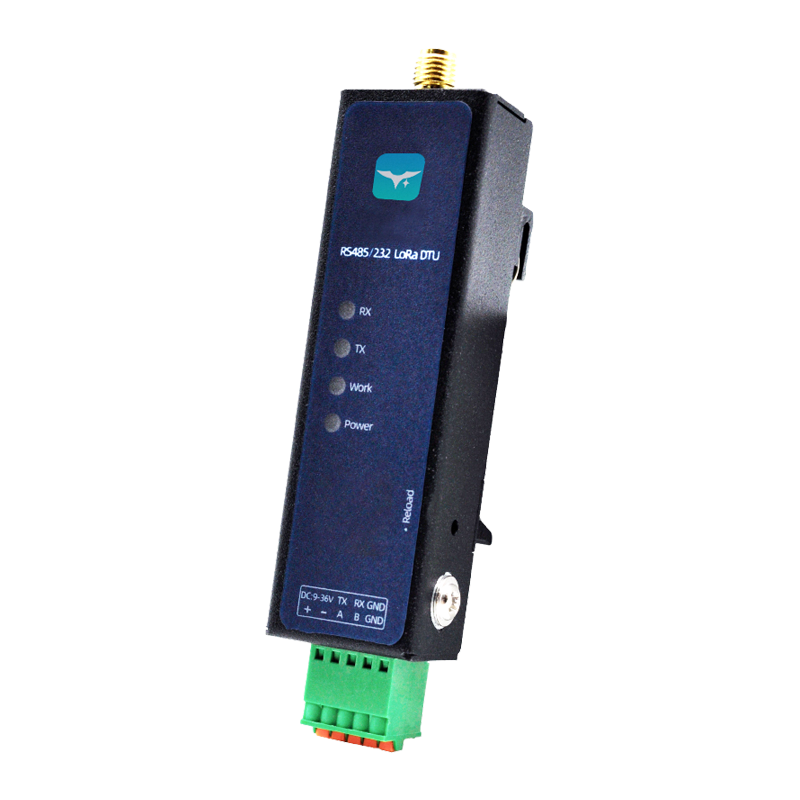

The Y210 is a low-frequency LoRa data radio that supports point-to-point communication protocols. It enables bidirectional data transmission between serial ports and LoRa. The operating frequency range is 410~493MHz. LoRa has the advantages of strong anti-interference capability and long transmission distance, with a communication range of up to 5KM. With a transmission power of up to 22dBm, this product can be applied in various industries and complex scenarios, such as power grids, transportation, fire protection, industrial production, meteorology, environment, agriculture, forestry, mining, and property management, etc.
Key Features
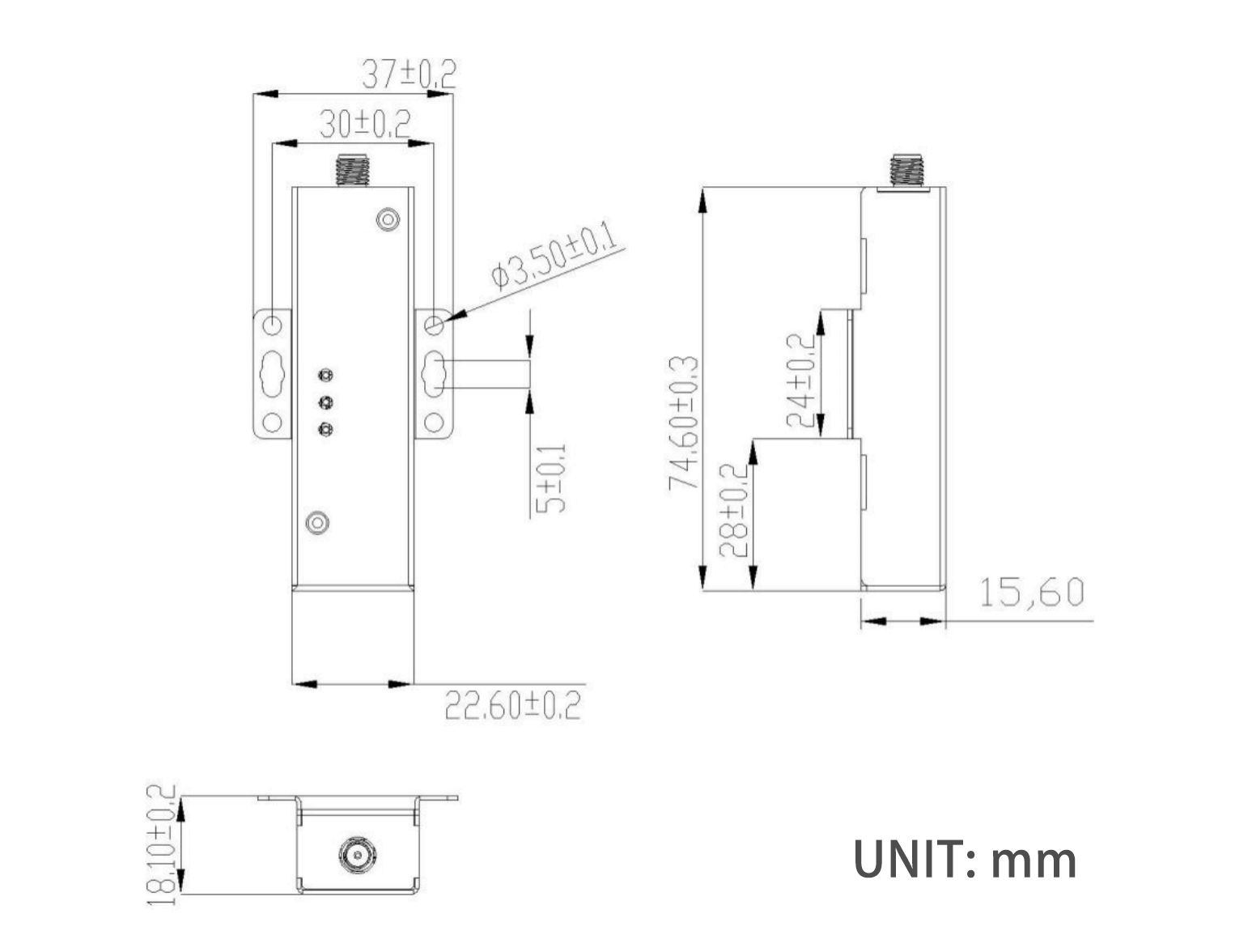
- Small size (74.622.618.1mm)
- Optional RS232/RS485/TTL interfaces
Key Attributes
| Item | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Parameters | Size | 74.6×22.6×16mm excluding side ears, antenna base, and terminals |
| Operating Temperature | -40~85°C | |
| Operating Humidity | 5%~95% | |
| Supply Voltage | 9~36V | |
| Receive Current | 20mA@12V | |
| Transmit Current | 40mA@12V | |
| RF Performance | Frequency Range | 410~493MHz |
| Transmit Power | 22dBm | |
| Serial Port | Interface Type | 3.3V TTL |
| Baud Rate | 1200~460800bps | |
| Parity | NONE/ODD/EVEN | |
| Data Bits | 7/8 | |
| Stop Bits | 1/2 | |
| Hardware Flow Control | NFC |
Dimensions
LoRa Parameter Description
To make the device simple and easy to use, the LoRa parameters mainly include start frequency, step size, channel, rate, operating mode, encryption key, and channel selection method. The specific explanations of these parameters are as follows:
Start Frequency: The initial frequency set for calculating the specific communication frequency of the device. The default is 410MHz. See the calculation method below.
- Step Size: The frequency interval between adjacent channels. The default is 1MHz.
- Channel: The device communication frequency is calculated as the start frequency plus the step size multiplied by the channel number. The default channel is 20.
- Operating Mode: Broadcast mode, point-to-point mode, and master-slave mode. The default is broadcast mode.
- Encryption Key: The encryption key for LoRa data transmission. It can only be set and cannot be queried. The length is 1-16 characters.
- Channel Selection Method: Set via AT command.
- Rate: Supports a total of 9 rates, from 1 to 9. The higher the number, the faster the rate, but the shorter the transmission distance. The default rate is 5.
LoRa Operating Modes
This series of products supports three operating modes: broadcast, point-to-point, and master-slave. The following are explanations of these modes:
1. Broadcast Mode
In broadcast mode, the device only broadcasts the data without changing its content. The advantage is that no transmission protocol is required, making it plug-and-play. In broadcast mode, point-to-point broadcast data transmission can be achieved by ensuring that both parties have the same channel, start frequency, step size, and rate.
The main AT commands used in broadcast mode are AT+FREQ, AT+CH, and AT+SPEED. For specific command explanations and usage methods, refer to the AT command section.
2. Point-to-Point Mode
In point-to-point mode, the transmission process includes a point-to-point transmission protocol, which allows flexible changes to the channel and target address when sending data, enabling point-to-point protocol transmission.
The transmission protocol is as follows: the data is in hexadecimal format. To send 3 bytes of data to the device with address 1 through channel 3, the last byte is the XOR value of all previous data: When the target address is FF FF, it is a broadcast communication in channel 3.
| Address (2 Bytes) | Channel (1 Byte) | Data (n Bytes) | Checksum (XOR, 1 Byte) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 01 | 03 | 01 02 03 | 02 |
| Address (2 Bytes) | Channel (1 Byte) | Data (n Bytes) | Checksum (XOR, 1 Byte) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FF FF | 03 | 01 02 03 | 03 |
The specific sending process in point-to-point mode is as follows:
When device A sends data to device B, device A sets its own channel according to the third byte of the communication protocol, encrypts the data, and sends it out. When device B receives the data, it judges and processes it according to the transmission protocol. The serial port only outputs the actual data part.
The main AT commands used in point-to-point mode are: AT+FREQ, AT+CH, AT+SPEED, and AT+ADDR. For specific command explanations and usage methods, refer to the AT command section.
3. Master Slave Mode
In master-slave mode, the master device needs to package the data according to the protocol format and send it to the slave device. When the slave device sends data to the master device, it can directly transmit the data without following the protocol. To reduce the packet loss rate of data sent from the master device to the slave device, the master device has a data retransmission mechanism, and the slave device automatically responds when receiving data without user intervention.
The transmission protocol is as follows: the data is in hexadecimal format. To send 3 bytes of data to the device with address 1:
| Address (2 Bytes) | Data (n Bytes) |
|---|---|
| 00 01 | 01 02 03 |
The specific sending process in master-slave mode is as follows:
When master device A sends data to slave device B, device A sends the data (following the transmission protocol). When device B receives the data, it judges it as its own data according to the transmission protocol, and the serial port only outputs the actual data part (i.e., 01 02 03). When slave device B needs to send data to device A, it can directly send the data without following the transmission protocol.
The main AT commands used in master-slave mode are: AT+FREQ, AT+CH, AT+SPEED, AT+ADDR, AT+RETRANS, and AT+TMODE. For specific command explanations and usage methods, refer to the AT command section.
Data Security
To ensure data transmission security between Y210 devices, the transmitted data is encrypted. The encryption key can be set using the AT+KEY command.